Glycogen Metabolism: Glycogenesis and MCQs for GPAT, NEET, CSIR NET, SSC Drug Inspector Exam
Glycogen is the major storage form of glucose mainly in the muscle and liver. Also most of the cells store minute amounts of glycogen. Glycogen is composed of glycosyl units which are linked by alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds.
The concentration of liver glycogen is greater than in muscle tissues; because muscle tissue comprises of large amount of mass, so its storage capacity is three to four times that of liver.
The formation and utilization of of glycogen in the body with the help of enzymatic system is called glycogen metabolism.
In this article we are going to study about 1 part of glycogen metabolism which is known as glycogenesis.
Glycogenesis
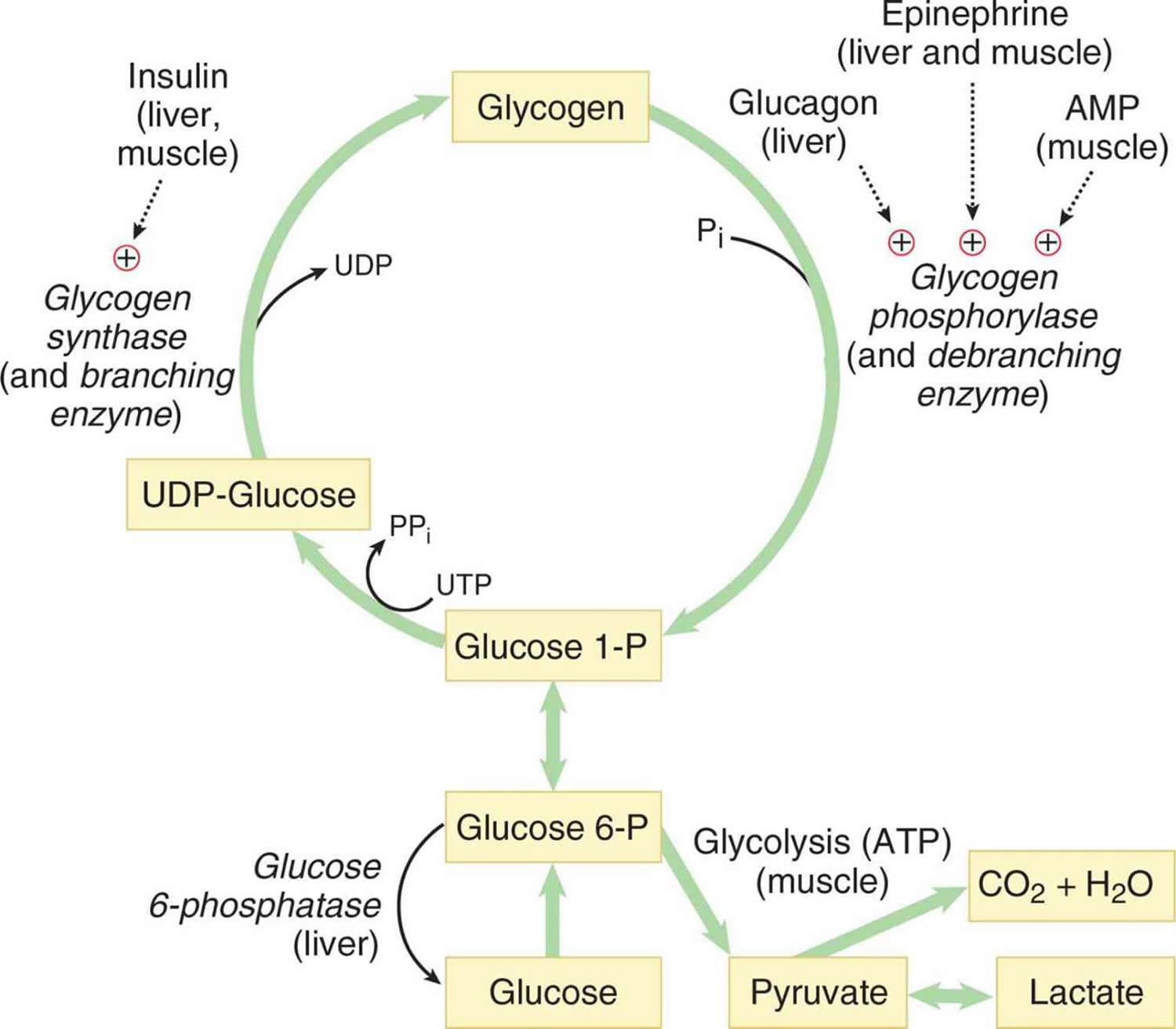
Glycogenesis is the pathway for the formation of glycogen from glucose. Glycogen is synthesized from glucose; the process requires energy which is supplied in the form of ATP and uridine triphosphate (UTP).
Location:- glycogenesis occurs in the cytosol of liver and muscle cells.
Pathway of glycogenesis and glycogenolysis
Reactions Of Glycogenesis
1. Glucose is phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate catalyzed by glucokinase (in liver) and hexokinase (in muscle).
2. Glucose-6-phosphate is converted to glucose-1-phosphate by phospho-gluco-mutase.
3. Glucose-1-phosphate reacts with UTP to form UDP-glucose and releases pyrophosphate. This reaction is catalyzed by UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase enzyme.
4. Now the glycogen synthase enzyme transfers the glucose monomer from UDP-glucose to the 4th position of glycogen primer to form alpha-1,4 glycosidic linkage.
5. The step 4 continues up to the chain elongated to minimum of 2nd monomer. after that the second enzyme known as branching enzyme transfers a portion of 1,4 chain to a near by branch to form 1,6 glycosidic linkage.
5. The branch again grow with 1,4 linkage using UDP-glucose and then further branching by 1,6 glycosidic linkage.
Regulation of Glycogenesis
The principal enzyme for controlling the glycogenesis is the glycogen synthase enzyme. This enzyme is regulated by several allosteric effectors like hormone and cyclic AMP.
Enzymes like epinephrine and glucagon inhibits the glycogenesis. Insulin inhibits the cAMP which further inhibits the glycogen synthase.
High concentration of Glucose-6-phosphate stimulates the synthesis of new glycogen.
Significance of Glycogenesis
- It removes the excess glucose from the circulation and store it in form of glucose.
- Keep blood glucose level normal
- Remove lactate from skeletal muscles and RBCs.
- Supply glucose at active skeletal muscle
- Replenish the liver glycogen
- Regulates acid base balance
Multiple choice questions (MCQs)
1. Why do glycogen metabolism takes place?
A. Carbohydrate metabolism
B. Fat metabolism
C. Lipid metabolism
D. Amino acid metabolism
2. Which enzyme is considered as the principal enzyme for the regulation of glycogenesis?
A. Phosphoglucomutase
B. Glycogen phosphorylase
C. Glucose-6-phosphatase
D. Glycogen synthase
3. Where glycogenesis takes place?
A. Cytosol
B. Mitochondria
C. Ribosomes
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
4. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. Glycogen metabolism is divided in 4 parts
B. Glycogenesis is synthesis of glycogen
C. Glycogen metabolism occurs in muscle and liver
D. The concentration of liver glycogen is greater than muscle tissue
5. What is the main function of hexokinase?
A. Glucose to glu-6-phosphate in muscle
B. Glucose to glucose-6-phosphate in liver
C. Both
D. None
6. Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction which is utilized In both glycogenesis and glycogenolysis?
A. Phosphoglucomutase
B. Glycogen phosphorylase
C. Glucose-6-phosphatase
D. Glucan transferase
7. Match the following-
a. Epinephrine 1. Inhibits cAMP
b. Insulin 2. Inhibits glycogen synthase
c. Glucose-6-phosphate 3. Inhibits glycogenesis
d. Glucagon 4. Stimulates glycogen synthase
8. Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of glucose-1-phosphate to UDPGlc?
A. UDPGlc pyrophosphorylase
B. UDPFlc dehydrogenase
C. Both A and B
D. None of the above
9. Which enzyme catalyzes the only reversible reaction of whole glycogen metabolism
A. Phosphoglucomutase
B. Glycogen phosphorylase
C. Glucose-6-phosphatase
D. Glucan transferase
10. Why muscle cannot release glucose into blood and is used exclusively by itself?
A. Muscles cannot do extra work
B. All glucose is used for muscle contraction
C. Absence of glucose-6-phosphatase
D. Both A and B
11. Which of the following stimulates the glycogenesis?
A. Epinephrine
B. Glucagon
C. Insulin
D. None of the above
12. Which form of energy inhibits the glycogenolysis?
A. FAD
B. cAMP
C. ATP
D. NADH
13. Which type of bond links the glycosyl units of glycogen compounds?
A. Hydrogen bonds
B. Covalent bonds
C. Glycosidic bonds
D. sometimes A and sometimes C
14. Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction of glycogenesis?
A. Hexokinase
B. Glycogen synthase
C. Glucokinase
D. All of the above
15. Where is glucose-6-phosphate mainly used?
A. Glycolysis
B. TCA cycle
C. HMP shunt
D. Both A and C
ANSWERS:-
1. Carbohydrate metabolism
2. Glycogen synthase
3. Cytosol
4. Glycogen metabolism is divided in four parts
5. Glucose to glu-6-phosphate in muscle
6. Phosphoglucomutase
7. a – 2 b – 1 c – 4 d – 3
8. UDPGlc pyrophosphorylase
9. Phosphoglucomutase
10. Absence of glucose-6-phosphatase
11. None of the above
12. cAMP
13. Glycosidic bonds
14. All of the above
15. Both A and C
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:– Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 182-187.