Hyperparathyroidism : Definition, Types, Symptoms, Treatment And MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF
“Hyperparathyroidism is a condition in which your parathyroid gland produces excess amount of parathyroid hormone in your bloodstream.”
1.] These glands are located behind the thyroid at the bottom of your neck, and are about the size of rice grain.
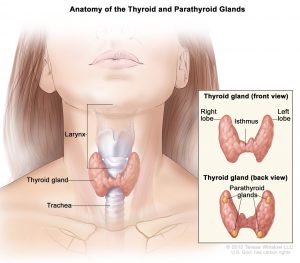
The above image is taken for education purpose only from niddk.nih.gov
TYPES :-
Basically, there are three types of hyperparathyroidism :
- Primary hyperparathyroidism : This hyperparathyroidism occur from the oversecretion of parathyroid hormone due to the disease of parathyroid gland.
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism : This secondary hyperparathyroidism is caused due to the disease in other parts of the body.
- Tertiary hyperparathyroidism : It develops from the secondary hyperplasia after removal of the cause of secondary hyperplasia.
SYMPTOMS :-
Signs and symptoms of hyperparathyroidism are as follows :-
- Osteoporosis
- Kidney stones
- Excessive urination
- Abdominal pain
- Tiring easily or weakness
- Depression or forgetfulness
- Bone and joint pain
- Frequent complaints of illness with no apparent cause
- Nausea, vomiting or loss of appetite
TREATMENT :-
Medications to treat hyperparathyroidism are as follows :
- Calciminimetics : A calciminimetic is a drug that mimics calcium circulating in the blood. The drug may trick the parathyroid gland into releasing less parathyroid hormone. This drug is sold as cinacalcet (Sensipar).
- Hormone replacement therapy : It is given to the women who have gone through menopause and have signs of osteoporosis, hormone replacement therapy may help bone to retain calcium.
- Biophosphates : They also prevent the loss of calcium from bones and may lessen osteoporosis caused by hyperparathyroidism.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS :-
1.] In MEN II B syndrome includes all except ?
a. Hyperparathyroidism
b. Marfanoid features
c. Medullary thyroid carcinoma
2.] Which of the following organ system would be affected by hyperparathyroidism ?
a. Digestive system
b. Excretory system
c. Musculoskeletal system
d. All of the above
3.] Disease which is caused due to excessive secretion of PTH is called ?
a. Hyposecretion
b. Hypersecretion
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
4.] Philip collip discovered which of the following hormone ?
a. Parathyroid hormone
b. Thyroxine
c. ADH
d. Oxytocin
5.] The vitamin which work along parathyroid hormone is ?
a. Vitamin – C
b. Tocopherol
c. Calciferol
d. Vitamin -B12
6.] Hypersecretion of parathyroid hormone result in ?
a. Stronger bones due to increased incorporation of calcium in them
b. Deposition of Ca in various skeletal structures
c. No effect on the constitution of bones
d. Weaker bones due to increased removal of Ca from them
7.] Deficiency of which of the following may cause bone deformation ?
a. PTH
b. Vitamin – D
c. STH
d. Thyroxine
8.] Function of thyrocalcitonin ?
a. To reduce the Ca level in blood
b. To increase the Ca level in blood
c. Oppose the action of thyroxine
d. Maturation of gonads
9.] Para – thyroid hormone is a ?
a. Peptide
b. Carbohydrate
c. Lipid
d. Steroid
10.] Parathormone induces ?
a. Increase in blood sugar level
b. Decrease in serum of Ca level
c. Increase in serum Ca level
d. Decrease in blood sugar level
SOLUTIONS :-
1.] (a) Hyperparathyroidism
2.] (d)
3.] (b) Hyperparathyroidism
4.] (a) Parathyroid hormone
5.] (c) Calciferol
6.] (d) Weaker bones due to increased removal of Ca from them
7.] (b) Vitamin – D
8.] (a) To reduce the Ca level in blood
9.] (a) Peptide
10.] (c) Increase in serum Ca level
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
REFERENCES :-
1.] Textbook Of Pathology By Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no. 806 – 807.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no. 1144 – 1147.