Hyperplasia: Definition, Pathological Hyperplasia, Physiologic Hyperplasia, Difference between Hyperplasia and Hypertrophy, Symptoms, Morphological Features and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF
“Hyperplasia is an increase in the number of cells in an organ or tissue, which may then have increased volume.”
1.] In hyperplasia the cellular population is capable of synthesizing DNA, thus permitting mitotic division, but in hypertrophy cell division is absent.
2.] Labile cells and stable cells can undergo hyperplasia while permanent cells have little or no capacity
3.] Pathologic Hyperplasia constitutes a fertile soil in which cancerous proliferation may eventually arise.

The above image is taken for educational purpose form dreamstime.com
PHYSIOLOGIC HYPERPLASIA: –
This physiologic hyperplasia is divided into two categories:
A.] Hormonal Hyperplasia: This type of hyperplasia can be understood by, the proliferation of the glandular epithelium of the female breast at puberty and during pregnancy, and the physiologic hyperplasia that occurs in the pregnant uterus.
B.] Compensatory Hyperplasia: This type of hyperplasia can be understood by, the hyperplasia that occurs when a part of liver is removed i.e., partial hepatectomy. Regeneration of epidermis after skin abrasion and hyperplasia in the nephron of the kidney are some other examples of Compensatory Hyperplasia.
PATHOLOGIC HYPERPLASIA: –
Most form of pathologic hyperplasia are instance of excessive hormonal stimulation or are the effect of growth factors in target cells.
An example of hormonal hyperplasia is hyperplasia in endometrium. After a normal menstrual period, there is a rapid burst of proliferative activity, which might be viewed as reparative proliferation or physiologic hyperplasia in the endometrium. This proliferation is potentiated by pituitary hormones and ovarian estrogen. It is brought to halt by the rising level of progesterone, usually about 10 to 14 days before the anticipated menstrual period.
In some, cases the above-mentioned balance between estrogen and progesterone is disturbed because of which there is absolute increase in the amount of estrogen, or both, with consequent hyperplasia of endometrium gland.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN HYPERPLASIA AND HYPERTROPHY: –
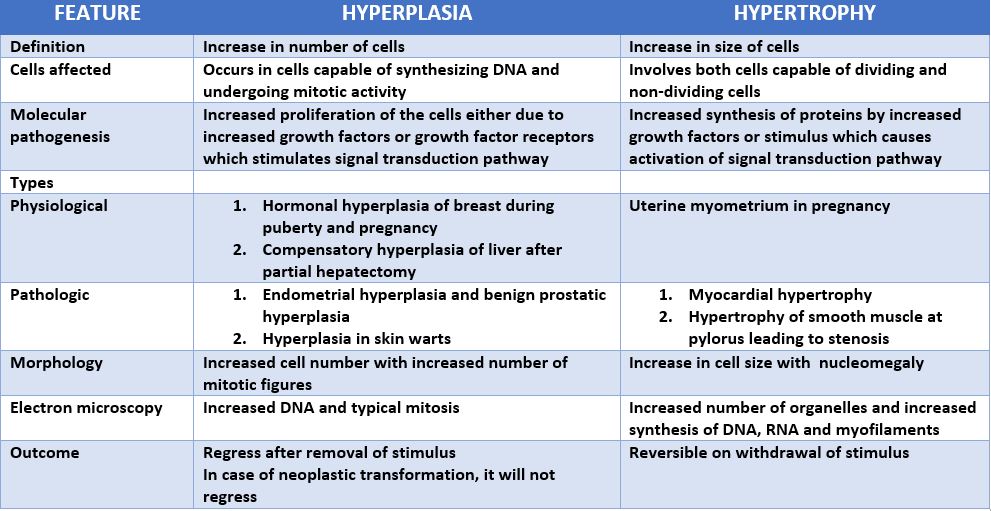
The above image is taken for educational purpose from histopatholgy.guru
SYMPTOMS OF HYPERPLASIA: –
Following are the symptoms of Hyperplasia:
- Abnormal menstrual bleeding
- Heavy bleeding during menstruation
- Acne
- Mood swings
- Excessive growth of body hairs
- Dryness in vagina
- Weak urine stream
- Frequent urination
- Leakage of urine
MORPHOLICAL FEATURES OF HYPERPLASIA: –
There is enlargement of the affected organ or tissue and increase in the number of cells. This is due to increased rate of DNA synthesis and hence increased mitoses of the cells.
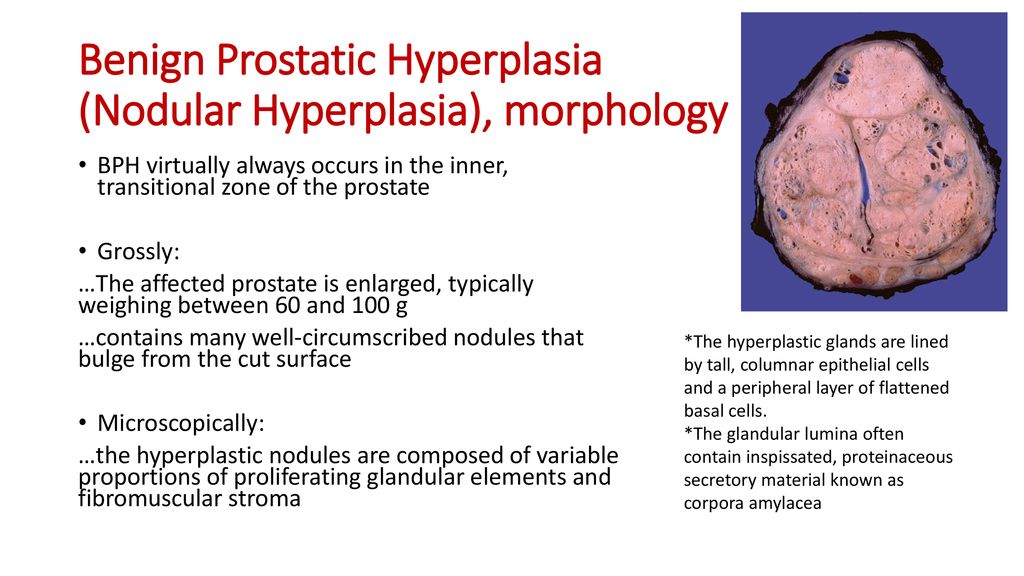
The above image is taken for education purpose from slideplayer.com
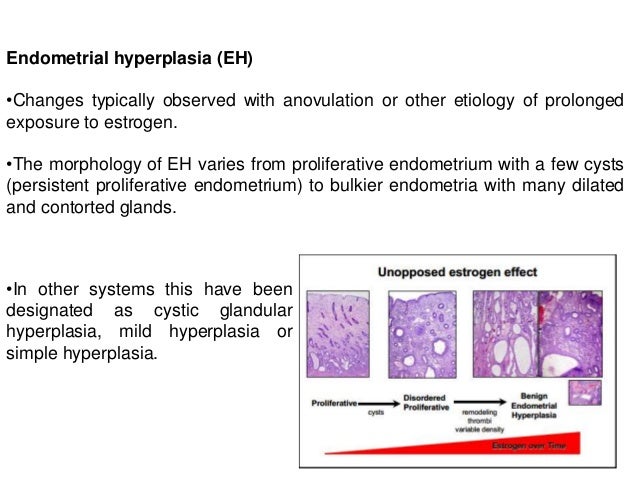
The above is taken for educational purpose form slideshare.net
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: –
1.] What is hyperplasia?
a. Increase in the number of cells
b. Increase in the size of the cell
c. Increase in organ size
d. None of the above
2.] In hyperplasia the cellular population is capable of synthesizing DNA, thus permitting mitotic division. Statement is True or False
a. True
b. False
3.] Which type of cell has little or no capacity of having Hyperplasia?
a. Labial cells
b. Permanent cells
c. Stable cells
d. All of the above
4.] When a part of liver is removed it is called?
a. Partial hepatectomy
b. Liver cirrhosis
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
5.] Which of the following are the example of compensatory hyperplasia?
a. Partial hepatectomy
b. Regeneration of epidermal cells
c. Hyperplasia of nephrons of the other kidney
d. All of the above
6.] Which of the following are the example of hormonal hyperplasia?
a. Hyperplasia of female breast at puberty
b. Hyperplasia of pregnant uterus
c. Prostatic hyperplasia in old age
d. All of the above
7.] What were the symptoms of hyperplasia?
a. Abnormal menstrual bleeding
b. Leakage of urine
c. Dryness in vagina
d. All of the above
8.] Which of the following are the example of endometrium hyperplasia?
a. Acne
b. Mood swings
c. Heavy bleeding during menstruation
d. All of the above
9.] Pathologic Hyperplasia constitutes a fertile soil in which cancerous proliferation may eventually arise. Above statement is True or False
a. True
b. False
10.] Leakage of urine is the symptom of which of the following type of hyperplasia?
a. Prostatic hyperplasia
b. Endometrium hyperplasia
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
SOLUTIONS: –
1.] (a) Increase in the number of cells
2.] (a)
3.] (b) Permanent cells
4.] (a) Partial hepatectomy
5.] (d)
6.] (d)
7.] (d)
8.] (d)
9.] (a)
10.] (a) Prostatic Hyperplasia
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCES: –
1.] Textbook of Pathology by Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no.39.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no.44 – 45.