LEVALLORPHAN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
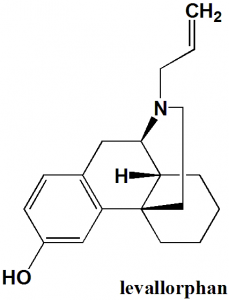
Levallorphan
IUPAC nomenclature
(−)-17-allylmorphinan-3-ol
Classification
- Levallorphan is an opioid antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 283.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Crystals from dilute ethanol |
| 3 | Melting point | 181°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Soluble in water; sparingly soluble in ethanol |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.48 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenanthrene, piperidine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 3 |
Mechanism of Action
Levallorphan acts as an antagonist for opioid mu receptors and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors α2 and α3.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR for opiates can be summarized as follows:
- Replacement of phenolic hydroxyl into –OCH3/-OC2H5 will make the drug less analgesic and cough suppression will also takes place.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCH3 makes the compound 5 times more active.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with -OC2H5 makes the compound 2.4 times more active than drug.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCOCH3 will also activate the compound by 4.2 times.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with ketone group inactivates the compound and makes it lesser active.
- By hydrogenation of alicyclic unsaturated linkage, activity increases by 1.2 times.
- On replacement of the methyl group from tertiary nitrogen by hydrogen atom, activity decreases.
- On replacement of N-CH3 by NCH2CH2Ph, activity increases by 14 times.
- When the methyl group of tertiary nitrogen replaced by N-allyl/methallyl/propyl, the compound so formed acts like the Drug antagonist.
- When the methyl group of tertiary nitrogen replaced by N(CH3)2 Cl– , compound have curare action and it do not possesses any analgesic activity.
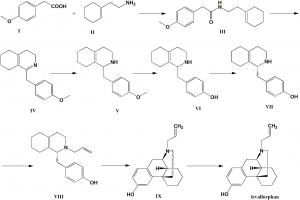
Method of synthesis
i. Homoanisic acid and 2-(cyclohexenyl group) ethanamine uses N, N’ carbonyls in aprotic polar solvents, preference temperature is that of dimimidazole process. It is then acylated and water is added. After that, Jing solvent extraction and drying to get the intermediate
ii. Intermediate III undergoes Bischler-napieralski ring closure reaction by dehtdrating agent followed by Jing alkalization to get intermediate
IV uses sodium borohydride for the reduction amination reaction. It is then alkalized with strong caustic in alcohol solvent. On drying, intermediate V is obtained.
iv. Product V undergoes hydrolysis and subsequent deethylation by48% hydrobromic acid solution. On Jing alkalization, intermediate VI is produced.
v. On splitting the intermediate VI with a resolving agent followed by rystallization and solvent alkalization produces intermediate
VII is basified under ketone solvent with an inorganic base followed by N-alkylation by 3-bromopropene to get intermediate compound
VIII undergoes Grewe cyclization and on alkalization produces intermediate IX which then gives levallorphan.[1]
Therapeutic Uses
Levallorphan is used for:
- As a general anesthesia
- Reverse the respiratory depression produced by opioid analgesics
- Induction of surgical anesthesia
Side Effects
Side effects Levallorphan are:
- Anxiety
- Hallucinations
- Confusions
- Dysphoria
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the Opiates.
| i. Replacement of phenolic hydroxyl into –OCH3/-OC2H5 will make the drug | A. More analgesic |
| ii. Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCH3 makes the drug | B. Less analgesic |
| C. Activity increases | |
| D. Activity decreases |
a) i-A, ii-C
b) i-A, ii-D
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-B, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Levallorphan: (−)-17-allylmorphinan-3-ol
- Diazepam: 7-Chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one.
- Atropine: (N-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl) 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate
- Diphenoxylate: ethyl 1-(3-cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)-4-phenylpiperidine-4-carboxylate.
a) TFFF
b) FTFT
c) TFFT
d) FTTF
Q.3 Correct statement related with the solubility of the drug Levallorphan from the following is?
a) Practically insoluble in water
b) Slightly soluble in water
c) Soluble in water
d) Very soluble in water
Q.4 Drug levallorphan acts as antagonist for which receptors?
a) Mu-opioid receptors
b) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors α2
c) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors α3
d) All of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is NOT a Medicinal use of drug Levallorphan?
a) As a general anesthesia
b) Antimalarial agent
c) Reverse the respiratory depression produced by opioid analgesics
d) Induction of surgical anesthesia
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Levallorphan: opioid antagonist
II. Haloperidol: Cholinolytic agent
III. Lorazepam: benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic
IV. Bitolterol: ß2-adrenergic agonist
a) I, III, IV
b) II, IV
c) II, III
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 Number of chiral carbons present in the structure of levallorphan?
a) 0
b)1
c) 2
d) 3
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-c
3-c
4-d
5-b
6-a
7-d