Metabolism of Acidic Amino Acid and MCQs for GPAT, NEET, CSIR NET, UPSC, SSC Exams
Metabolism of glutamic acid
Glutamic acid is a non-essential glucogenic amino acid.
Synthesis of glutamic acid
Glutamic acid is synthesized from alpha-ketoglutarate (an intermediate of TCA cycle) by
- Transamination (reaction A from below given picture)
- By reductive animation of ketoglutarate by NH4, catalyzed by glutamate dehydrogenase. (reaction B from below given picture)
Catabolism of glutamic acid
when glutamate is cleaved or broken, it is converted back to alpha-ketoglutarate by either transamination or dehydrogenase reaction.
Significance of glutamic acid
- Amino acids like glutamine, proline and arginine are derived from glutamate
- Glutamate is involved in synthesis of glutathione. Glutathione in turn is involved in transport of amino acid into kidney and intestinal cells.
- Glutamate is decarboxylated to form amine gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA serves as a neurotransmitter.
Metabolism of Glutamine
synthesis of Glutamine:- Glutamine is the amide of glutamate. It is produced from glutamate from glutamate synthetase . This enzyme adds ammonia to the carboxyl group of the side chain and hence forms the amide.
Degradation of Glutamine:- It is again recovered from glutamate only but using different enzyme. The enzyme used is glutaminase; which is particularly important in the kidney.
Metabolism of Aspartic Acid
Aspartic acid is non-essential glucogenic amino acid Synthesis of aspartic acid. Aspartate is synthesized from oxaloacetate (an intermediate from TCA cycle) by transamination reaction. Catabolism or degradation of aspartic acid Since transamination reaction is easily reversible, so aspartate is converted back to oxaloacetate.
Functions of aspartic acid
- In urea cycle, aspartate reacts with citrulline to form arginosuccinate; which in turn forms arginine and fumerate.
- Aspartate reacts with inosine mono-phosphate (IMP) to form AMP
Metabolism of Aspargine
Synthesis of Aspargine:- Aspargine is an amide of aspartate. It is formed from the aspartate by a reaction in which glutamine provides nitrogen for the formation of amide group.
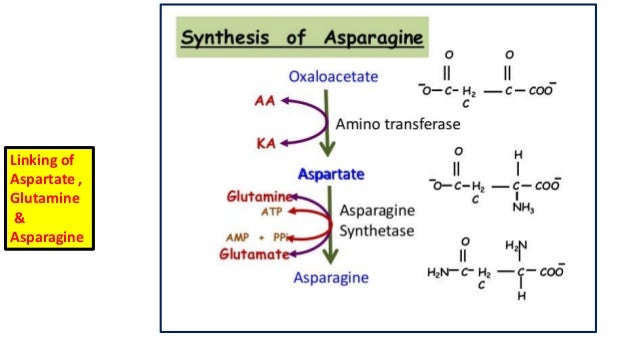
Degradation of Aspargine:- The amide nitrogen of aspartate is released as ammonia and aspartate by hydrolytic release. This reaction is done by asparginase enzyme.
Multiple choice questions (MCQs)
1. Glutamic acid is nutritionally which type of amino acid?
A. Essential amino acid
B. Non-essential amino acid
C. Semi-essential amino acid
D. Both A and C
2. Glutamic acid is synthesized from which compound?
A. Oxaloacetate
B. Pyruvate
C. Alpha-ketoglutarate
D. Aspartic acid
3. Which enzyme catalyzes the reductive amination of ketoglutarate?
A. Glutamate dehydrogenase
B. Glutamate oxidase
C. Glutamate transferase
D. None of the above
4. Which product is formed after the degradation of glutamic acid? A. Oxaloacetate
B. Pyruvate
C. Alpha-ketoglutarate
D. Aspartic acid
5. Which compound is involved in the synthesis of glutathione?
A. Oxaloacetate
B. Pyruvate
C. Alpha-ketoglutarate
D. Glutamic acid
6. Proline is derived from which compound?
A. Oxaloacetate
B. Glutamic acid
C. Alpha-ketoglutarate
D. Aspartic acid
7. Aspartic acid is nutritionally which type of amino acid?
A. Essential amino acid
B. Non-essential amino acid
C. Semi-essential amino acid
D. Both A and C
8. Match the following enzyme and its substrate-
a. Aspartate transminase 1. aspartate
b. Glutamate dehydrogenase 2. L-glutamate
c. Glutaminase 3. Alpha-ketoglutarate
d. Asparginase 4. Aspartate + alpha-ketoglutarate
9. Glutamine is synthesized from which compound?
A. Aspartic acid
B. Glutamate
C. Lysine
D. Histidine
10. Glutaminase is particularly important in which organ?
A. Kidney
B. Brain
C. Liver
D. Shoulder
11. Which of the following is major transporter of ammonia?
A. Aspartic acid
B. Glutamate
C. Lysine
D. None of the above
12. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. Proline is derived from aspartic acid
B. Aspartate reacts with citrulline to form arginosuccinate
C. Glutamine is major transport form of ammonia
D. Aspargine is formed from aspartate
13. Aspartate is synthesized from which compound?
A. Oxaloacetate
B. Pyruvate
C. Alpha-ketoglutarate
D. Glutamic acid
14. Which compound reacts with inosine monophosphate to form AMP?
A. Oxaloacetate
B. Pyruvate
C. Aspartic acid
D. Glutamic acid
15. Which of the following amino acid is glucogenic amino acid?
A. Aspartic acid
B. Glutamic acid
C. Proline
D. All of the above
ANSWERS:-
1. Non-essential amino acid
2. Alpha-ketoglutarate
3. Glutamate dehydrogenase
4. Alpha-ketoglutarate
5. Glutamic acid
6. Glutamic acid
7. Non-essential amino acid
8. a – 4 b – 3 c—2 d – 1
9. Glutamate
10.Kidney
11. None of the above
12. Proline is derived from aspartic acid
13. Oxaloacetate
14. Aspartic acid
15. all of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:– Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 292-293.