VALPROIC ACID Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Valproic acid or Valproate
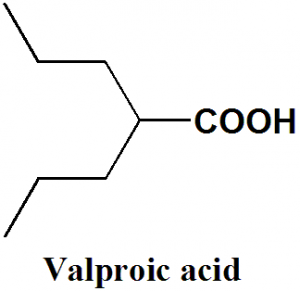
IUPAC nomenclature
2-propylpentanoic acid
Classification
Valproic acid is a fatty acid derivative and an anticonvulsant drug.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 144.21g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Clear colorless liquid |
| 3 | Boiling point | 222°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Very soluble in organic solvents. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.75 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Not present |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Valproic acid inhibits succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase which results n increase in succinic semialdehyde which is an inhibitor of GABA transaminase. Due to this, the metabolism of GABA is decreases and there is increase in GABAnergic neurotransmission. Which results in an increased inhibitory activity. There is a direct suppression of the voltage gated sodium channel activity and indirect suppression through effects on GABA.
- Valproic acid impacts the extracellular signal-related kinase pathway which results in the phosphorylation of ERK1/2. This activation increases expression of several downstream targets including ELK-1 with subsequent increases in c-fos, growth cone-associated protein-43 which contributes to neural plasticity, B-cell lymphoma/leukaemia-2 which is an anti-apoptotic protein, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) which is also involved in neural plasticity and growth. There is increase in neurogenesis and neurite growth due to valproic acid.
- There is also a downstream effect of increased BDNF expression which leads to increase in GABAA receptors which contribute further to increased GABAergic activity.
- It also exerts a non-competitive indirect inhibitory effect on myo-inosital-1-phosphate synthetase. Due to this, there is reduced de novo synthesis of inositol monophosphatase and depletion of inositol.
- Valproate also produces down regulation of protein kinase C proteins which are related with the bipolar disorder. PKC inhibition also contributed in migraine prophylaxis.
- Valproic acid also impacts the fatty acid metabolism and there is less incorporation of fatty acids substrates in sterols and glycerolipids which impacts the membrane fluidity and there is increase in action potential threshold which contributes to the drug’s antiepileptic action.
- Valproic acid also acts as a direct histone deacetylase inhibitor. Hyperacetylation at correlates with te improvements in the symptoms of bipolar patients.
Structure Activity Relationship
- 3,3,4-trimethylpentanoic acid is also as active as valproic acid.
- Increasing chain length increases the anticonvulsant activity.
- Double bond introduction decreases the activity of the drug.
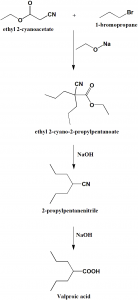
Method of synthesis
i. Alkylation of cyanoacetic ester with 2 moles of propylbromide tp produce dipropylcyanoacetic ester.
ii. Hydrolysis and decarboxylation of the above formed compound produces dipropylacetonitrile.
iii. On further hydrolysis, valproic acid is produce.
Therapeutic Uses
Valproic acid is used for:
- Treatment of seizures
- Treatment of manic phase of bipolar disorder
- Prevention of migraine headaches
Side Effects
Side effects of Valproic acid are:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Diarrhea
- Loss of hair
- Blurred vision
- Double vision
- Changes in menstrual periods
- Tremors
- Ringing in ears
- Unsteadiness
- Weight loss or gain
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts
- Mood changes
- Encephalopathy
- Weakness
- Vomiting
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the drug Valproate.
| i. Increasing the chain length | A. Increases anticonvulsant activity |
| ii. Introduction of the double bond | B. Decreases the anticonvulsant activity |
| C. Increases the activity of drug | |
| D. Decreases the activity of drug |
a) i-A, ii-C
b) i-A, ii-D
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-B, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Valproic acid: 2-propylhexanoic acid
- Triflupromazine: N,N-dimethyl-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-10H-phenothiazin-10-yl]propan-1-amine.
- Loxapine: 8-Chloro-11-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-5H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4]diazepine
- Tiotixene: (9Z)-N,N-dimethyl-9-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propylidene]-9H-thioxanthene-2-sulfonamide.
a) TTFF
b) FTFT
c) TTFT
d) FTTF
Q.3 Correct statement related with the solubility of the drug Valproic acid from the following is?
a) Practically insoluble in Organic solvent
b) Sparingly soluble in organic solvent
c) Soluble in organic solvent
d) Freely soluble in organic solvent
Q.4Correct statement related with the mechanism of action of valproate is?
a) Impacts the metabolism of carbohydrates
b) Impacts the metabolism of nucleic acid
c) Impacts the metabolism of fatty acids
d) Impacts the metabolism of Vitamins
Q.5 Which amongst the following is not a therapeutic use of drug Valproic acid?
a) Treatment of Seizures
b) Treatment of manic phase of bipolar disorder
c) Treatment of migraine headaches
d) Treatment of diarrhea
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Valproate: Succinimide anticonvulsant drug
II. Aspirin: Anti-inflammatory drug
III. Triflupromazine: Phenothiazine antipsychotic drug
IV. Carbamazepine: Morphine analogue
a) I
b) II, IV
c) II, III
d) II, IV
Q.7 Valproic acid is produced by hydrolysis of?
a) Dipropylacetonitrile
b) Propylacetonitrile
c) Pentanoic acid
d) Butanoic acid
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-b
2-b
3-d
4-c
5-d
6-a
7-a