IBUPROFEN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
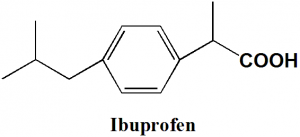
Ibuprofen
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-2-(4-(2-Methylpropyl)phenyl)propanoic acid
Classification
- NSAID
- Propionic acid derivative
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 206.28 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Colorless crystalline solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 75-77°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Very soluble in alcohol |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.97 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Ibuprofen is a nonselective COX inhibitor, which means it inhibits both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes.
- COX-2 inhibition leads to decreases in production of prostaglandins which is responsible for the transmission of pain signals in the body and mediating inflammation, fever and swelling.
- Side effects of ibuprofen like GI ulceration are caused due to inhibition of COX-1 enzyme.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of ibuprofen can be summarized as follows:
- Anti-inflammatory activity of the drug can be increased and related side effects can be reduced by substitution of n α-methyl group on the alkanoic acid portion of acetic acid derivatives.
- Ibuprofen is less hepatotoxic and more potent than ibufenac.
- (+)-enantiomer possess greater activity than (-)-enantiomer.
- Eudismic (S/R) ration for the inhibition of bovine prostaglandin synthesis is 160. [1]
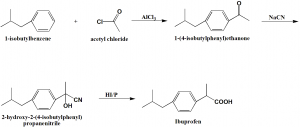
Method of synthesis
i. Acylation of isobutylbenzol by acetyl chloride to give iso-butylbenzophenone.
ii. Iso-butyl benzophenone is reacted with sodium cyanide to produce oxynitrile.
iii. On reaction of oxynitrile with hydroiodic acid in the presence of phosphorus to give ibuprofen, which subsequently undergoes phases of dehydration, reduction and hydrolysis.[2]
Therapeutic Uses
Ibuprofen is used for:
- Relieving headache
- Relieving dental pain
- Relieving pain due to menstrual cramps
- Relieving muscle aches
- Relieving pain due to arthritis
- Reducing fever
- Relieving pain due to common cold and flu
- Relieving pain due to minor injuries
Side Effects
Side effects of ibuprofen are:
- Allergic reactions
- Skin reactions
- Shortness of breath
- Vision changes
- Nausea
- Upset stomach
- Loss of appetite
- Bloating
- Gas
- Jaundice
- Pale skin
- No urination
- Anemia
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Ringing sounds in ears
MCQs
Q.1 “(RS)-2-(4-(2-Methylpropyl)phenyl)propanoic acid” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Anileridine
b) Ibuprofen
c) Paracetamol
d) Amphetamine
Q.2 Physical appearance of Ibuprofen is?
a) Oily liquid
b) Pale yellow crystals
c) Colorless liquid
d) Colorless crystalline solid
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Ibuprofen | A. Carbamate cholinesterase inhibitor |
| ii. Neostigmine | B. ß-adrenergic blocker |
| iii. Atenolol | C. Benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic |
| iv. Zolpidem | D. NSAID |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
c) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
d) i-C, ii-D, iii-A, iv-B
Q.4 Correct statements from below which are related with the mechanism of action of ibuprofen can be??
I. It is a selective COX inhibitor
II. Side effects of drug is due to COX-1 inhibition
III. Therapeutic action is due to COX-2 inhibition
IV. COX inhibition results in increased production of prostaglandins
a) I ,IV
b) III, II
c) IV , I
d) II , III
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of drug Ibuprofen can b?
- Anti-inflammatory activity of the drug can be increased and related side effects can be reduced by substitution of n α-methyl group on the alkanoic acid portion of acetic acid derivatives.
- Ibuprofen is more hepatotoxic and less potent than ibufenac.
- (+)-enantiomer possess lesser activity than (-)-enantiomer.
- Eudismic (S/R) ration for the inhibition of bovine prostaglandin synthesis is 160
a) TFFT
b) FFTF
c) FTFT
d) FTTF
Q.6 Number of chiral carbons in the structure of Ibuprofen is?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.7 The drug Ibuprofen is mainly used for?
a) Reducing headache
b) Relieving pain due to menstrual cramps
c) Reducing fever
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-b
2-d
3-b
4-d
5-a
6-b
7-d