Hypoparathyroidism : Definition, Types, Symptoms, Treatment And MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF
“Hypoparathyroidism is an uncommon condition in which your body produces abnormally low level of parathyroid hormone (PTH).”
1.] PTH is an key to regulate and maintain the balance of two minerals in your body i.e; calcium and phosphate.
2.] Low production of PTH will lead to low level of calcium in blood and bones and an increase level of phosphorous in your blood and bones.
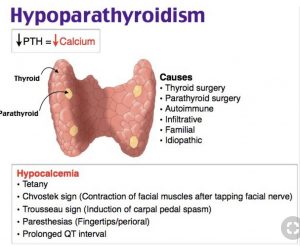
The above image is taken for education purpose only from printerest.com
TYPES :-
Basically, there are three types of hypoparathyroidism :
- Primary Hypoparathyroidism : Primary hypoparathyroidism is caused by the disease of parathyroid gland. Most common cause of primary hypoparathyroidism are – surgical procedures involving thyroid, parathyroid, or radial neck dissection for cancer.
- Pseudo Hypoparathyroidism : In pseudo – hypoparathyroidism, the tissue fails to respond to parathyroid hormone though parathyroid gland are usually normal. It is an rare inherited condition with an autosomal dominant character.
- Pseudopseudo Hypoparathyroidism : It is an another rare familial disorder in which all the clinical features of the pseudo hypoparathyroidism are present except that these patients have no hypocalcaemia or hyperphosphataemia and tissue respond normally to parathyroid hormone.
SYMPTOMS :-
Signs and symptoms of hypoparathyroidism are as follows :
- Tingling and burning in your fingertips, toes and lips
- Fatigue and weakness
- Painful menstrual periods
- Patchy hair loss
- Dry, coarse skin
- Brittle nails
- Depression or anxiety
- Muscle aches or cramps in your legs, feet, face or stomach
- Spasm on your muscle
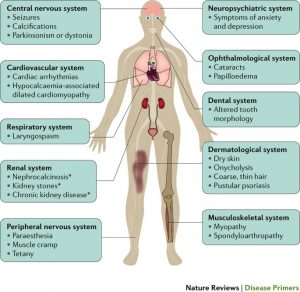
The above image is taken for education purpose only from nature.com
TREATMENT :-
The goal of treatment is to relive the symptoms and to normalize the level of calcium and phosphorous in your body. A treatment usually includes :
- Oral calcium carbonate tablets
- Vitamin – D as it help body to absorb calcium and eliminate phosphorous.
- Magnesium.
- Thiazide diuretics as it can decrease the amount of calcium lost through your urine.
- Parathyroid hormone (Natpara).
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS :–
1.] The secretion of PTH in man is regulated by ?
a. Circulating level of Na
b. Circulating level of Ca
c. Circulating level of K
d. Circulating level of Mg
2.] The hormone responsible for the regulation of Ca and P metabolism is secreted by ?
a. Pancreas
b. Thyroid
c. Thymus
d. Parathyroid
3.] Hypothyroidism in adults causes ?
a. Addison’s disease
b. Myxoedema
c. Sterility
d. Cretinism
4.] Parathormone regulates ?
a. Blood calcium level
b. Ca phosphate level
c. Body temperature
d. None of the above
5.] Parathormone deficiency in man causes ?
a. Hyper calcemia
b. Hypo calcemia
c. Goiter
d. All of the above
6.] Removal of parathyroids in human begins result in ?
a. Tetany
b. Simmonds’s disease
c. Myxoedema
d. Addison’s disease
7.] Hormone that decrease the calcium level in blood ?
a. Thyroxine
b. Parathormone
c. Thyrocalcitonin
d. Cortisol
8.] Parathormone deficiency leads to ?
a. Decrease Ca2+ level in blood
b. Increase of Ca2+ level in blood
c. Osteoporosis
d. Hypercalemia
9.] Parathormone controls ?
a. Fatty acid metabolism
b. Na and K metabolism
c. Ca and P metabolism
d. Protein metabolism
10.] Parathyroid hormone is ?
a. Is produced by thyroid gland
b. Is released when blood Ca level fails
c. Stimulates osteoblasts to lay down new bone
d. Stimulates calcitonin release
SOLUTIONS :-
1.] (b) Circulating level of Ca
2.] (d) Parathyroid
3.] (b) Myxoedema
4.] (b) Ca phosphate level
5.] (b) Hypo calcemia
6.] (a) Tetany
7.] (c) Thyrocalcitonin
8.] (a) Decrease of Ca2+ level in blood
9.] (c) Ca and P level metabolism
10.] (b) Is released when blood Ca level fails
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
REFERENCES :-
1.] Textbook Of Pathology By Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no. 807 – 808.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no. 1147 – 1148.