Anatomy and functions of Liver and Pancreas and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse, Pharmacist Exam
PANCREAS
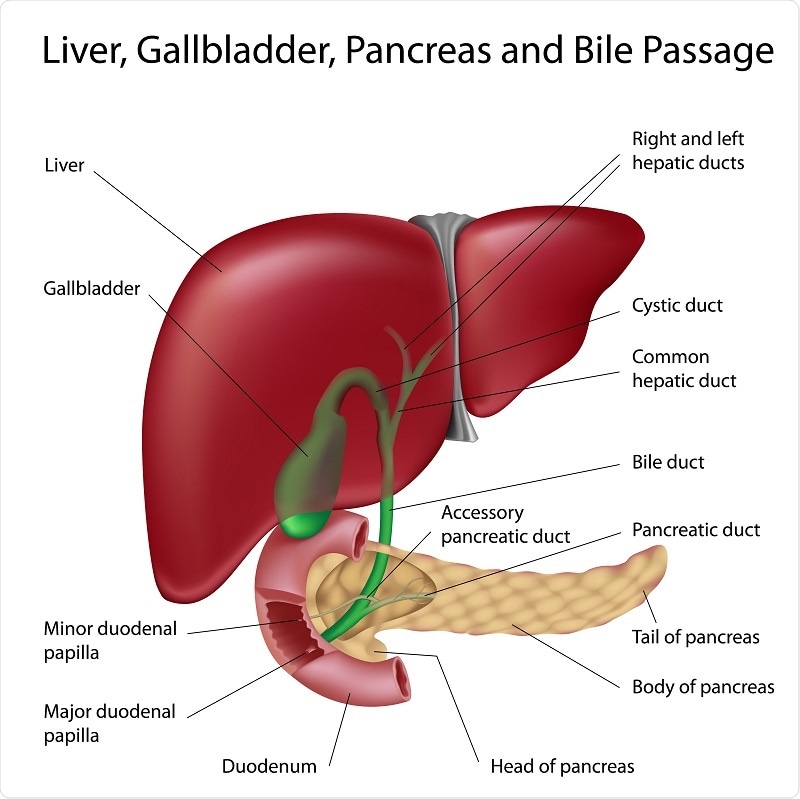
The pancreas is a pale grey gland which is situated in the epigastric and left hypochondriac region of abdominal cavity. It weighs around 60g and is about 12-15cm long. It consist of broad head, a body and the narrow tail. The abdominal aorta and the inferior vena cava lies behind the gland. The pancreas comes under both exocrine as well as endocrine gland.
The exocrine pancreas:- It consist of large no. of lobules, each lobule drained into a tiny duct and all these tiny duct further forms a pancreatic duct which extends the whole length of the gland and meets the duodenum. Just before entering the duodenum, the pancreatic duct joins the common bile duct to form hepatopancreatic ampulla.
The function of exocrine pancreas is to produce pancreatic juice which contains enzymes that digest carbohydrates, proteins nd fats. The parasympathetic stimulation increases the secretion of pancreatic juice
The endocrine pancreas:- the endocrine pancreas consist of group of specialized cells known as pancreatic islets. The islets have no ducts so the hormones release directly enters into the blood. The endocrine pancreas secretes two hormones- insulin and glucagon which controls the blood glucose level.

LIVER
The liver is the largest gland in the body which weighs about 1-1.3kg. it is situated in the upper part of the abdominal cavity. Its upper an anterior surfaces are smooth and curved so that it fits into the diaphragm while the posterior surface have irregular outlines.
The liver is surrounded by a thin inelastic capsule and partially it is covered by the peritoneum. The liver is held in position partly the by ligaments formed from the peritoneum folds and partly by the pressure of the organs in the abdominal cavity. The liver has four lobes- the right lobe, left lobe, caudate and quadrate. The portal fissure is the posterior surface of the liver from where the arteries, veins nerves etc enters and leave the liver.
The lobes of liver are formed from the tiny functional unit known as lobules. These are formed from the hepatocytes arranged in the pairs of column. Between every two pairs of columns of cells are the sinusoids which contain the mix blood-oxygenated as well as deoxygenated blood. The blood formed than reaches the liver cells. Among the cells that lines the sinusoids are the hepatic macrophages which destroys the worn out cells and also destroys the foreign particles. Lymphoid tissue and the lymph vessels are also present in each lobule.
Functions of liver
The functions of liver includes-
- Carbohydrate metabolism:- the liver maintains the blood glucose levels. When the level rises, the glucose is converted to glycogen and is stored done by the hormone insulin. Later when the glucose level falls glucagon converts the glycogen back to glucose and the level is maintained.
- Fat metabolism:- fats are converted into suitable form in which they are used to supply energy.
- Protein metabolism:- this occur in 3 steps
- Deamination of amino acids
- Transamination
- Synthesis of plasma proteins
- Breakdown of erythrocytes and defence against microbes:- carried out by hepatic macrophages.
- Detoxification of drugs and toxic substances
- Inactivation of hormones
- Storage:- stored substances are glycogen, fat soluble vitamins, iron, Cu and some water soluble vitamins
- Secretion of bile:- the hepatocytes synthesis the constituents of bile from the mixed arterial and venous blood in the sinusoids. The bile canaliculi are found between the columns of liver cells. All these canaliculi join up to form the right and left hepatic ducts from where the bile drains from the liver. The liver secretes about 500-1000ml of bile daily. The constituents of bile include- water, mineral salts, mucus, bile pigments, bile salts and cholesterol.
Multiple choice questions(MCQ)
1. where is pancreas situated?
A. epigastric region of abdominal cavity B. left hypochondriac region of abdominal cavity
C. pelvic cavity D. both A and B
2. the pancreatic duct of the exocrine gland extends till?
A. duodenum b. jejunum
C. ileum D. fundus
3. what is the function of insulin and glucagon?
A. maintains potassium level B. maintains Ca level
C. maintain glucose level D. skeleton growth
4. Match the following organs associated with liver-
a) diaphragm 1. superiorly
b)stomach 2. inferiorly
c) oesophagus 3. posteriorly
d) lower ribs 4. Laterally
5. Which of the following structure is associated with liver?
A. common bile duct B. portal vein
C. pancreatic duct D. none of the above
6. where is the liver situated?
A. upper part of abdominal cavity B. lower part of abdominal cavity
c. in front of the abdominal cavity d. behind the abdominal cavity
7. Which of the following statement is true?
A. the endocrine pancreas consist of islets
B. the diaphragm is associated inferiorly
C. the internal carotid arteries supply the pancreas
D. the liver has 5 lobes.
8. What is the weight of liver?
A. 2kg B. 500g
c. 1kg D. 3Kg
9. what is the function of liver?
A. carbohydrate metabolism B. storage
C. production of heat D. all of the above
10. which of the following is not the constituent of bile?
A. urea B. cholesterol
C. mucus d. water
ANSWERS:-
- Both A and B
- duodenum
- maintain glucose level
- a – 1 b – 2 c – 3 d – 4 .
- none of the above
- upper part of abdominal cavity
- the endocrine pancreas consist of islets
- 1kg
- all of the above
- urea
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFERENCE:- Ross and Wilson-Anatomy and physiology in health and illness; 12th edition; page no.-:308-312.