TOLTERODINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
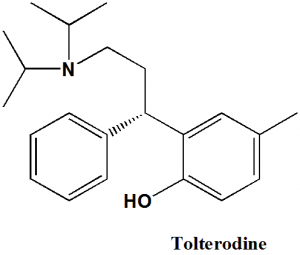
Tolterodine
IUPAC nomenclature
(S)-2-[3-(Diisopropylamino)-1-phenylpropyl]-4-methylphenol.
Classification
Tolterodine is an acetylcholine antagonist. It is a muscarinic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 325.5 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 205°C. |
| 4 | Solubility | 12 mg/ml in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 5.6 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Benzene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Tolterodine and its metabolites act as competitive antagonist at muscarinic receptors.
- Due to antagonism of muscarinic receptors, there is inhibition of bladder contraction, decreases in detrusor pressure and incomplete emptying of the urinary bladder. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
- The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
- Most potent derivatives has X as an ester.
- X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
- The N substituent can be quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine or both with different alkyl groups.
- Maximum potency obtained when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon units.
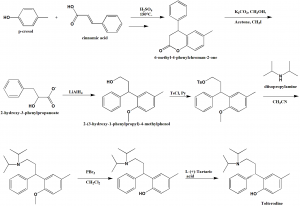
Method of synthesis
i. Condensation of p-cresol with cinnamic acid in tetralone media, in presence of sulfurinc acid at higher temperatures to produce 6-methyl-4-phenylchroman-2-one.
ii. Lactone ring opening with methanol and phenolic hydroxyl etherification to give 2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoate.
iii. The latter compound undergoes reduction to give 2-(3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropyl)-4-methylphenol.
iv. The last compound formed is tosylated with tosyl chloride in pyridine.
v. The product is reacted with diisopropylamine in acetonitrile to give an amine.
vi. Methyl fragment of amine is cleaved with phosphorous tribromide in dichloromethane to give a recemic mixture of tolterodine.
vii. Racemic tolterodine is resolved using tartaric L-(+)-tartaric acid to get the desired tolterodine. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Tolterodine is used for:
- Treatment of Overactive bladder
- Reduce leakage of urine
- Reduce the feelings of needing to urinate
Side Effects
Side effects of Tolterodine are:
- Dry mouth
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Blurred vision
- Nervousness
- Stomach upset
- Headache
- Dry eyes
MCQ
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Tolterodine?
a) (S)-2-[1-[2-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)ethyl] pyrrolidin-3-yl] -2,2-diphenyl-acetamide
b) (S)-2-[3-(Diisopropylamino)-1-phenylpropyl]-4-methylphenol.
c) 7-Chloro-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid
d) N,N-Dimethyl-2-[6-methyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl]acetamide hemitartrate
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of Tolterodine?
I. Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
II. The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
III. Poorest derivatives has X as an ester.
IV. X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
a) I, II
b) III
c) III, IV
d) II
Q.3 Corrects sequence of the steps involved in the synthesis of Tolterodine from p-cresol?
I. Condenstation with cinnamic acid
II. Tosylation
III. Reaction with diisoropylamine
IV. Lactone ring opening with methanol and esterification
V. Reduction
VI. Methyl fragmentation of amine using phosphorous tribromide
a) II – I – III – IV- VI – V
b)IV- II – I – III – VI – V
c) I- IV – V- II – III – VI
d) VI- I – II – IV- V – III
Q.4 Side effects of drug Tolterodine is/are?
a) Constipation
b) Headache
c) Dry mouth
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with their correct molecular weights-
| i. Darifenacin | A.426.5 gm/mol |
| ii. Tolterodine | B.307.4gm/mol |
| iii. Chlorazepate | C. 325.5 gm/mol |
| iv. Zolpidem | D. 314.72 gm/mol |
a) i-C, ii-B, iii-A, iv-D
b) i-C, ii-B, iii-D, iv-A
c) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
Q.6 An example of drug from class Acetylcholine antagonist?
a) Zolpidem
b) Chlorazepate
c) Amphetamine
d) Tolterodine
Q.7 The type of ring system found in the structure of Tolterodine?
a) Dihydrobenzofurane
b) Pyrrolopyrimidine
c) Benzene
d) Pyrrolopyrrole ring
Participate in Free Online Test for GPAT, Pharmacist,Drug Inspector
ANSWERS
1-b
2-b
3-c
4-d
5-c
6-d
7-c
REFERENCES
[1] Todorova A, Vonderheid‐Guth B, Dimpfel W. Effects of tolterodine, trospium chloride, and oxybutynin on the central nervous system. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 2001 Jun;41(6):636-44. [2] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of best-seller drugs. Academic press; 2016 Jan 7.