The post Human Anatomy and Physiology-Study Material, Notes and MCQ for NEET, GPAT, Paramedical Staff Recruitment appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>Here you can find free study material related to Human Anatomy and Physiology
- Disorders of HEART: Types, Causes, and treatments MCQ for NEET, GPAT, NET JRF, GATE, RRb Pharmacist Exam
- Epithelial Tissue and MCQ for NEET, GPAT, NET JRF, GATE, Staff Nurse and Pharmacist Exam
- Physiology of Vision, Visual Pathways and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, NIPER JEE
- Anatomy of Male Reproductive System and Question answer for NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse Exam
- Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestine Anatomy and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, NIPER, Staff Nurse Exam
- Physiology of Hearing and Equilibrium and MCQ for NEET,GPAT, Nursing exams, Pharmacist Recruitment
- Cardiac Cycle and Question Answer for NEET, GPAT, Nursing, Pharmacist and Lab Technician Exam
- Adrenal Glands Anatomy and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse, Pharmacist & Lab Technician Exam
- Anatomy and Physiology of NOSE and TONGUE
- Female reproductive system and MCQ for NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse,Lab Technician exam
- Anatomy of EAR and Multiple choice question for NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse, SSC exam, Lab Technician exam
- Anatomy and functions of KIDNEYS and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, SSC, GATE, RRB Pharmacist,
- Pituitary gland, Hypothalamus and Their Hormone and Multiple choice question for NEET, AIIMS, GPAT
- Urine formation and MCQs for NEET Exam, Pharmacist, GPAT, Nursing Exam , SSC Exam
- Thyroid and Parathyroid glands and MCQs for NEET, SSC, GPAT, LAB Technician, Pharmacist Exams
- Anatomy of EYE and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, RRB Pharmacist, Staff Nurse Exam
- CONNECTIVE TISSUES AND MCQs for NEET, GPAT, Pharmacist, UGC NET JRF Exams
- Lymphatic Organs and Tissues; Question answer for NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse Exam
- Cardiac Output, Stroke Volume, Heart Rate and its Regulation and Multiple choice questions
- Anatomy of Skin, Layer of Epidermis and Dermis and Important Questions for Exam
- Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in External and Internal Respiration; MCQ With Answer
- Blood Pressure and the factors affecting BP and MCQs With Answers
- Anatomy of LUNGS and MCQs for NEET, GPAT,Nursing Exams
- LARYNX: Anatomy and function and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, UGC NET JRF
- Anatomy and Functions of PHARYNX and MCQs for NEET, Pharmacist & Drug Inspector Exams
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM, Abnormal ECG AND MCQs based on Heart Problems
- BLOOD GROUPS, BLOOD TYPES AND MCQs Asked in Pharmacist, Drug Inspector and GPAT Exams
- JOINTS and MCQs
- Muscular Tissue-Skeletal muscle tissue and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, GATE and NET JRF Exam
- Acid-Base balance In Urinary System and MCQ for NEET, GPAT CSIR NET JRF and GATE Lifesciences Exam
- Transport of Oxygen and Carbon-dioxide During External and Internal Respiration and MCQ
- Hemostasis and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, Pharmacist,SSC and Staff Nurse Exam
- Components of Blood and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, Pharmacist and Staff Nurse Exam
- Homeostasis and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, Pharmacist,SSC, CBSE Biology and Staff Nurse Exam
- Chromosomes, Genes and DNA:MCQs For NEET, GPAT, Pharmacist, Staff Nurse Exam
- Disorders of kidney and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, Pharmacist, Staff Nurse,NIPER Exam
- Disorders of Endocrine Glands and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, Pharmacist, Staff Nurse Exam
- Disorders of Lungs and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, Pharmacist, Staff Nurse,NIPER Exam
- Parts of BRAIN: Diencephalon, Brain Stem and Cerebellum and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, Pharmacist, Staff Nurse Exam
- Pancreatic islets, Pineal gland, Local hormones and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, SSC, Pharmacist and Staff Nurse Exam
- The Reproductive Cycle, Puberty and Menopause; MCQ for NEET, GPAT, SSC, Pharmacist and Staff Nurse Exam
- Protein Synthesis and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, SSC, Pharmacist and Staff Nurse Exam
- Blood Circulation and Conduction system and MCQs NEET,GPAT, SSC, Pharmacist and Staff Nurse Exam
- Anatomy and functions of Liver and Pancreas and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse, Pharmacist Exam
- Anatomy of Ureters, Urinary Bladder and Urethra and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, Pharmacist, and Staff Nurse Exam
- Introduction to Central Nervous System Anatomy and MCQs for NEET, GPAT and Competitive Exams
- Nervous Tissue Anatomy and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF, Staff Nurse Exam
- Parts of BRAIN: CEREBRUM Anatomy and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse, Lab Technician and SSC Exam
- Cranial Nerves Anatomy and MCQs For NEET, SSC, GPAT, Staff Nurse and CSIR NET JRF Exam
- Spinal Nerves Anatomy and MCQs For NEET, SSC, GPAT, Staff Nurse and CSIR NET JRF Exam
- Autonomic Nervous system(ANS) Anatomy and MCQs For NEET, GPAT,SSC, DBT BET, CSIR NET JRF
- Cell Division and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF Exam
- Spinal Cord Anatomy and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, NET JRF, Nursing Exams
- AXIAL SKELETON: Hyoid bone, Vertebral column and Thorox and MCQs for NEET, GPAT
- Transport across Plasma Membrane of CELL and MCQs for NEET, GPAT and CSIR NET JRF Exam
- AXIAL SKELETON: Cranial and facial bones and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse, Pharmacist and Lab Technician Exam
- APPENDICULAR SKELETON and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF, Paramedical Staff Exam
The post Human Anatomy and Physiology-Study Material, Notes and MCQ for NEET, GPAT, Paramedical Staff Recruitment appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>The post Muscular Tissue-Skeletal muscle tissue and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, GATE and NET JRF Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>- Skeletal muscle tissue:- these muscle moves the bones of skeleton; these are striated (alternating light and dark bands appear ). These muscles are controlled by somatic division, and they are voluntary in nature
- Cardiac Muscle tissue:- as the name suggest, they form most of the heart wall. These are controlled by autonomic nervous system and are involuntary in nature.
- Smooth muscle:- These muscles form the internal structures like blood vessels, airways and some organs of abdominal cavity. They are non-striated. These are controlled by ANS and are involuntary in nature.
Functions of muscular tissue includes-
- produces body movements,
- stabilizes body positions,
- storage and movement of substances within body and also generates heat.
Properties of muscular tissue are:–
-
- electrical excitability,
- contractility,
- extensibility and elasticity.
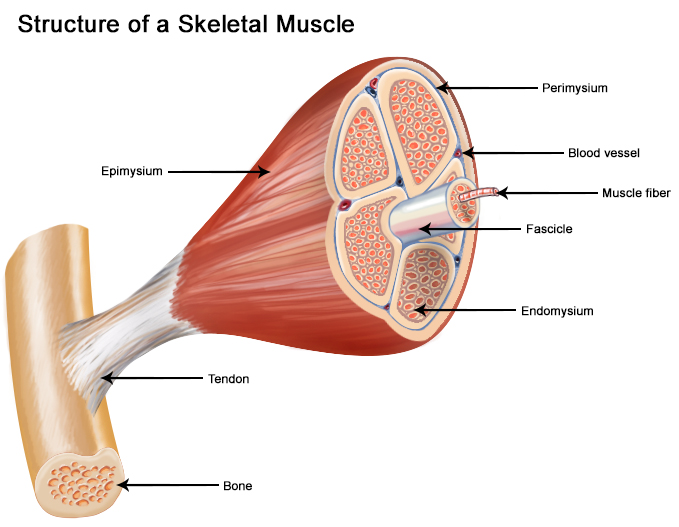
Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Skeletal muscle is made up of thousands of muscular cells also known as muscle fibers. Skeletal muscle are surrounded and protected by connective tissue. The hypodermis, which separates the skin and muscle are made of areolar connective tissue. Fascia is a dense sheet of irregular connective tissue that lines the body wall. Their are three layers of connective tissue around the skeletal muscle-
- Epimysium:- it is the outermost layer which encloses the entire muscle and are made of dense irregular connective tissue.
- Perimysium:- they surrounds group of 10-100 muscle fibers and separates them into fascicles; and are made of dense irregular connective tissue.
- Endomysium:- the innermost layer which separates one muscle fiber from another; and are made of areolar connective tissue.
The sarcolemma is the plasma membrane of muscle fiber and consist of multiple nuclei. Transverse tubules are the tiny invaginations of sarcolemma. Within the sarcolemma is the sarcoplasm, the cytoplasm of muscle fiber. Sarcoplasm is comprised of large amount of glycogen. Glycogen is a large molecule which is composed of many glucose; which in turn helps in ATP synthesis. The sarcoplasm also contains a red-colored protein known as myoglobin; This protein is only found in muscle fiber and binds the oxygen molecules.
The sarcoplasm is filled with thread like structures known as myofibrils. these are the contractile organelles of skeletal muscle. Within the myofibrils are smaller structure known as filaments. the think filaments are 8nm in diameter and thick filaments are 16nm in diameter. Both thick and thin filaments are involved in contractile process.


(All Figure used only for Educational Purpose)
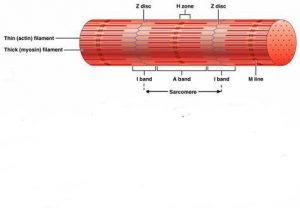
The filaments inside the myofibrils do not extend over the entire length of the muscle fibers, rather they are present in compartments known as sarcomeres. These sarcomere are basic functional unit of myofibrils.
- The Z-discs are narrow plate-shaped regions of dense protein, they separates one sarcomere from another.
- The middle darker part Is the A- band which extends the entire length of thick filaments.
- The I-band is a lighter and less dense part which consist thin filaments but no thick filaments.
- At the center of each A-band , is a H-zone which contains all thick filaments but no thin filaments.
- M-line is present in the center of H-zone is at the middle of each sarcomere.
Myofibrils are made of 3 types of proteins-
- Contractile protein:-these proteins generate force of contraction. The two contractile proteins are myosin and actin
- Regulatory protein:- these proteins controls that when will be the contractile process be on and off. there are two regulatory proteins:tropomyosin and troponin.
- Structural protein:- these proteins keeps the thin and thick filaments in proper alignment. these are: titin, alpha-actinin myomesin, nebulin and dystrophin.
Skeletal Muscle Contraction Cascade
Difference between all muscle tissue
Difference between 3 type of muscle fibers
Multiple choice questions(MCQs)
1. Skeletal muscle tissues are controlled by?
A. somatic division B. parasympathetic division
C. CNS D. sympathetic division
2. Muscle cells are also known as?
A. myofibrils B. Filaments
C. muscle Fibers D. none of the above
3. What is the diameter of thick filaments?
A. 10nm B. 16mm
C. 12nm D. 16nm
4. Which of the following muscle tissue are voluntary in nature?
A. cardiac muscle B. smooth muscle
C. autorhythmic muscle D. none of the above
5. What is the main function of myoglobin?
A. extensibility B. elasticity
C. binds O2 together D. both A and C
6. Match the following-
A. Z-disc 1. Contains all thin filaments
B. I- band 2. Separates two sarcomere
C. A-band 3. Contains thick filaments no thin filaments
D. H-zone 4. Entire length of thick filaments
7. What is the function of muscular tissue?
a. storage B. movement of bones
C. stabilize body position D. all of the above
8. What is the function of structural proteins?
a. generates contractile force b. controls contraction
C. proper alignment of filaments D. binds O2
9. Which of the following statement is true?
A. titin is one of the regulatory protein
B. storage is one of the properties muscular tissue
C. sarcomere are the functional unit of myofibril
D. H-zone contains all thin filaments
10. What separates one sarcomere from another?
A. I-band B. H-zone
C. Z-discs D. A-band
ANSWERS:-
1. somatic division
2. muscle fibers
3. 16nm
4. none of the above
5. binds 02 together
6. A – 2 B – 1 C – 4 D – 3
7. all of the above
8. proper alignment of filaments
9. sarcomere is the functional unit of myofibril
10. Z-disc
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Reference:-Gerard J. Tortora -Principles of anatomy and physiology; edition twelfth ; page no.-: 302-310.
The post Muscular Tissue-Skeletal muscle tissue and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, GATE and NET JRF Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>